Hedging Uniswap V3 Positions with Options
Overview
In this article, we’ll look at how options can be used to hedge Uniswap positions.
Introductory terms:
- Underlying asset — the asset being considered; in our case, a token.
- To hedge — to protect against risk. When a user holds a risky asset (for example, ETH, an open position on Uniswap, etc.), the value of their portfolio depends on the asset’s price. To hedge a position means to make it less dependent on the risk factor (in this case, the asset price).
Uniswap V3 position
Let’s recall how Uniswap V3 works. Liquidity providers set a desired price range in which their provided tokens will be used, earning fees from swaps. The narrower the range, the more fees the position earns per swap. However, with a narrow range, the price will leave it faster, and then the position won’t earn anything.
When someone swaps one token for another—for example, USDC for WETH—there are more dollars and fewer ethers in the pool. That is, the amount of the appreciated asset becomes smaller, and the amount of the depreciated one becomes larger, and this happens in every Uniswap V3 position that was active at the moment of the swap. Accordingly, the total portfolio value of the liquidity provider changes.
Liquidity provider risk profile
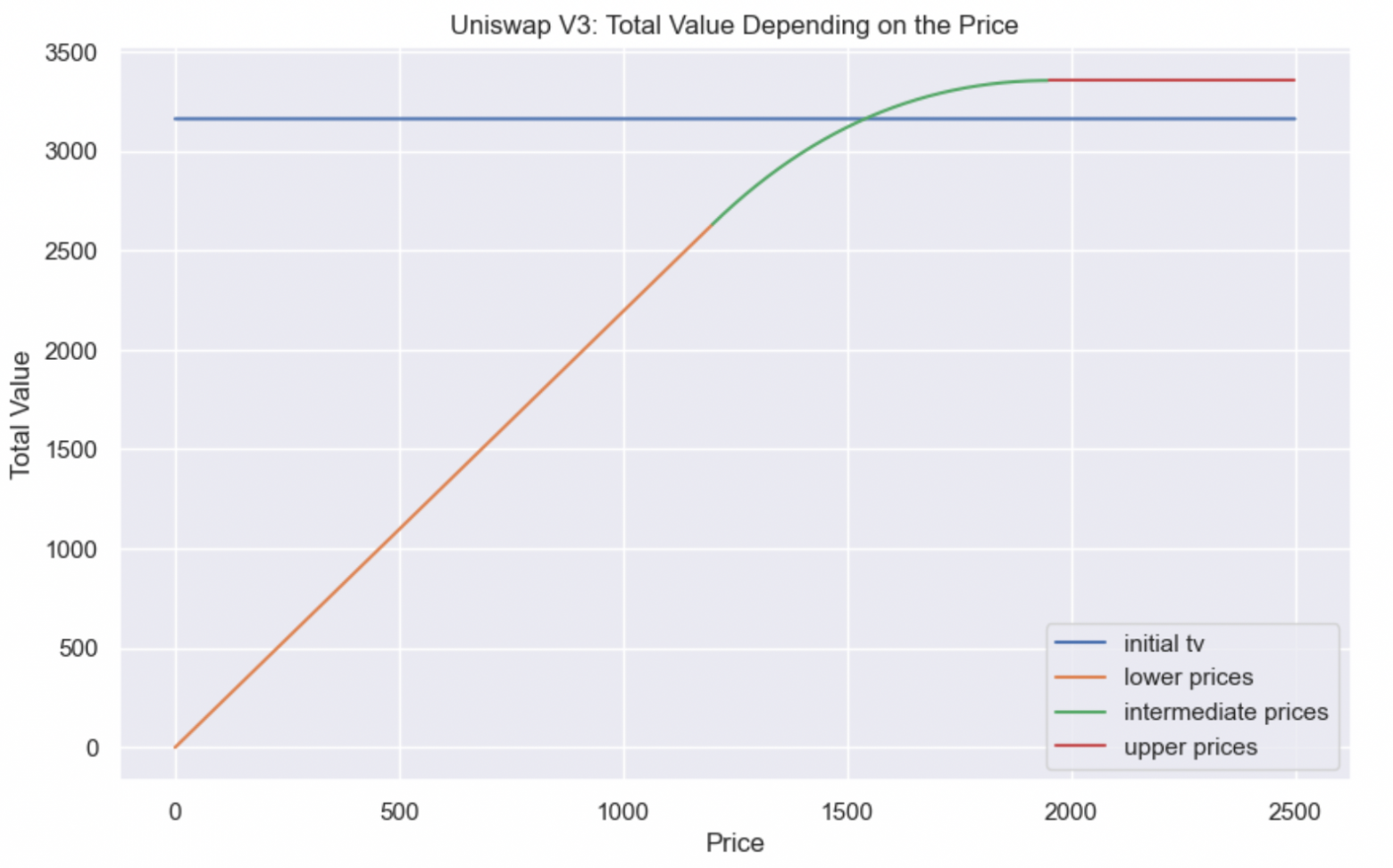
Let’s consider how the value of a liquidity provider’s position depends on the price of ETH:
What’s the problem with such a position?
The problem is that if the price goes down, the liquidity provider will lock in more and more loss. At first, due to the curvature of the Uniswap V3 position (while the price is within the range), the loss won’t be as strong, but as the price moves down the loss will increase more and more.
This means that the liquidity provider has open risk on the price of the underlying asset.
What can be done?
We can buy an option, and thanks to it the liquidity provider won’t depend so much on the price of the underlying asset.
What is an option?
An option is a contract that gives the right (but not the obligation) to buy/sell the underlying asset at a pre-agreed moment in time for a pre-agreed price.
What’s important here is that the buyer has the right, but not the obligation. That is, at the moment of option expiry they may choose not to exercise the option—for example, if exercising is unprofitable for them.
In this article we will consider only European options, i.e., those that can be exercised only at the moment the option expires.
Options come in two types: the first type gives the right to buy, the second type gives the right to sell (at a fixed moment in time for a fixed price).
In our case, to hedge the liquidity provider, we need an option that gives the right to sell (a put option).
How to calculate the option payoff
Payoff is how much we will earn/lose if we buy this option.
The payoff of a European put option at expiry is determined by the formula:

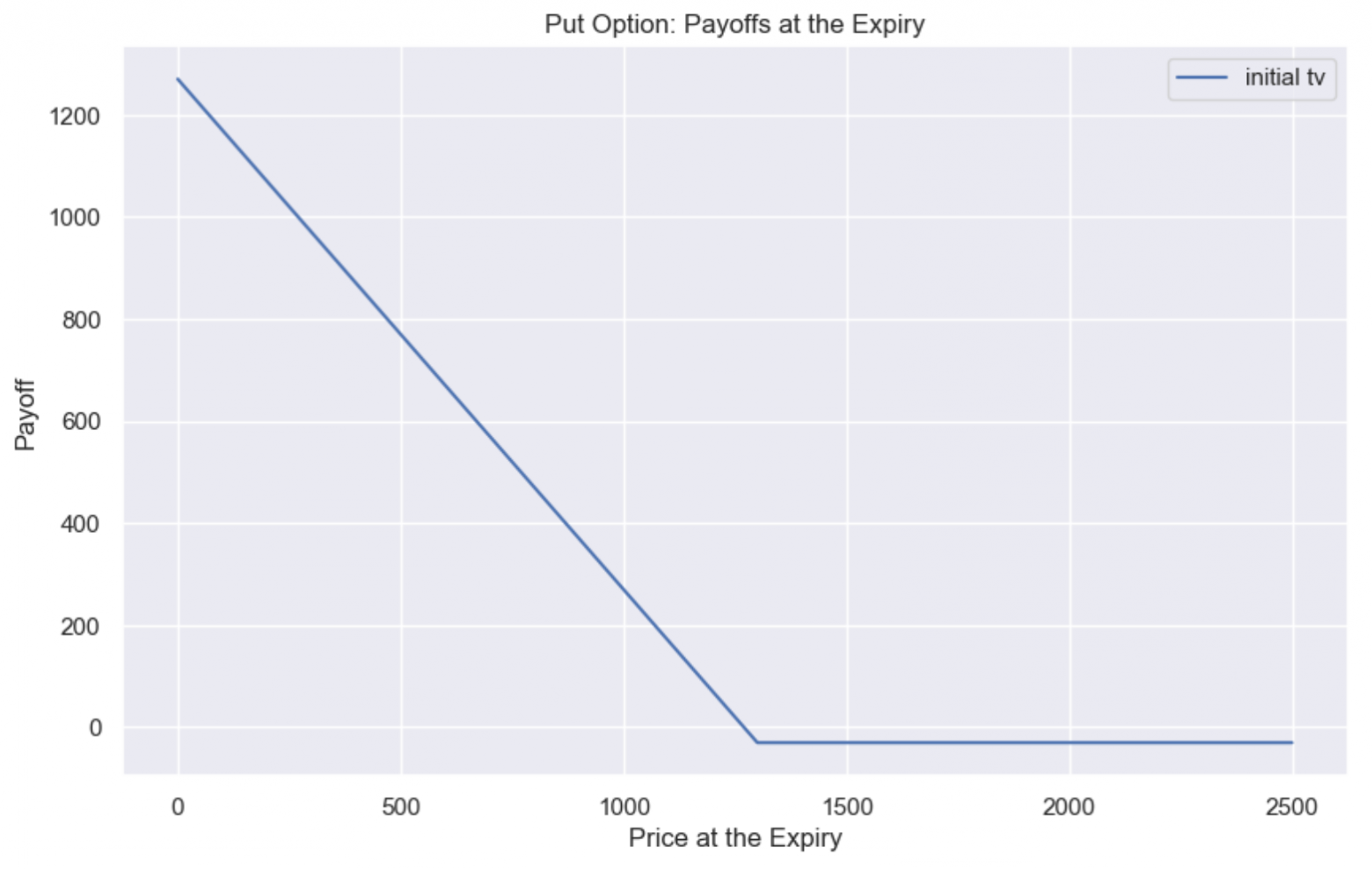
The payoff depending on the price at the moment of exercising the option will look like this:
What’s notable here?
Such an option gives a positive payoff when the underlying asset price falls, and in the Uniswap V3 position we are considering we lose money when the price moves down.
So let’s “buy” such an option—i.e., add the two graphs together—and see what happens:
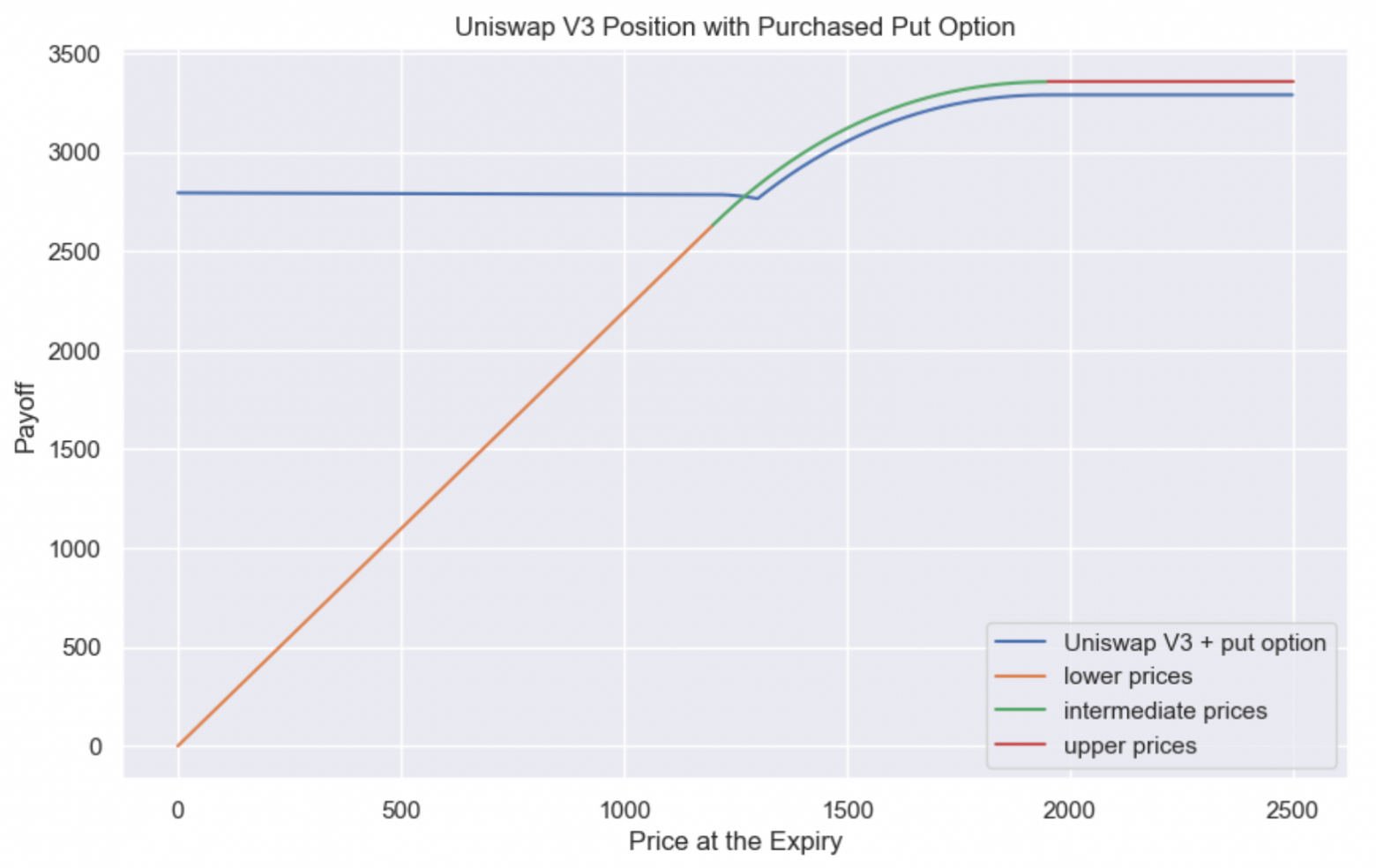
In the example above, we bought not one option, but 1.8, so that in total the Uniswap V3 position and the option would produce an almost horizontal graph.
Important:
- In this example, the option price was taken “out of thin air”, purely to show how hedging with an option works.
- The more “in the money” the purchased option is, the higher its purchase cost will be (which is logical—after all, if at an ETH price of 1500 the option gives the right to buy at 1200, it shouldn’t be cheap).
Is it possible to fully hedge a Uniswap V3 position?
The answer is yes. You can choose a put option with such a strike and expiration that it hedges the Uniswap V3 position with very good accuracy. Usually this should be an option with a longer expiration.
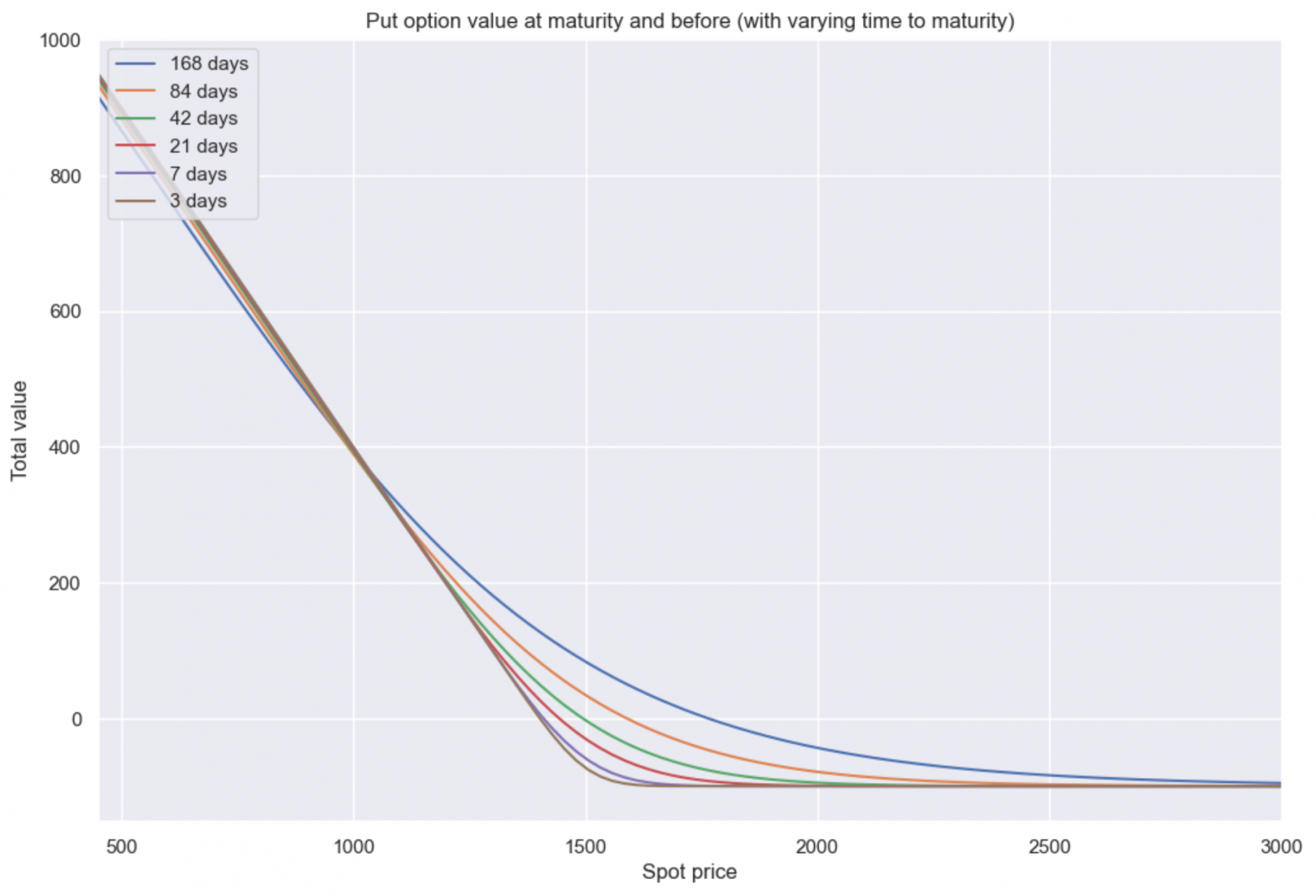

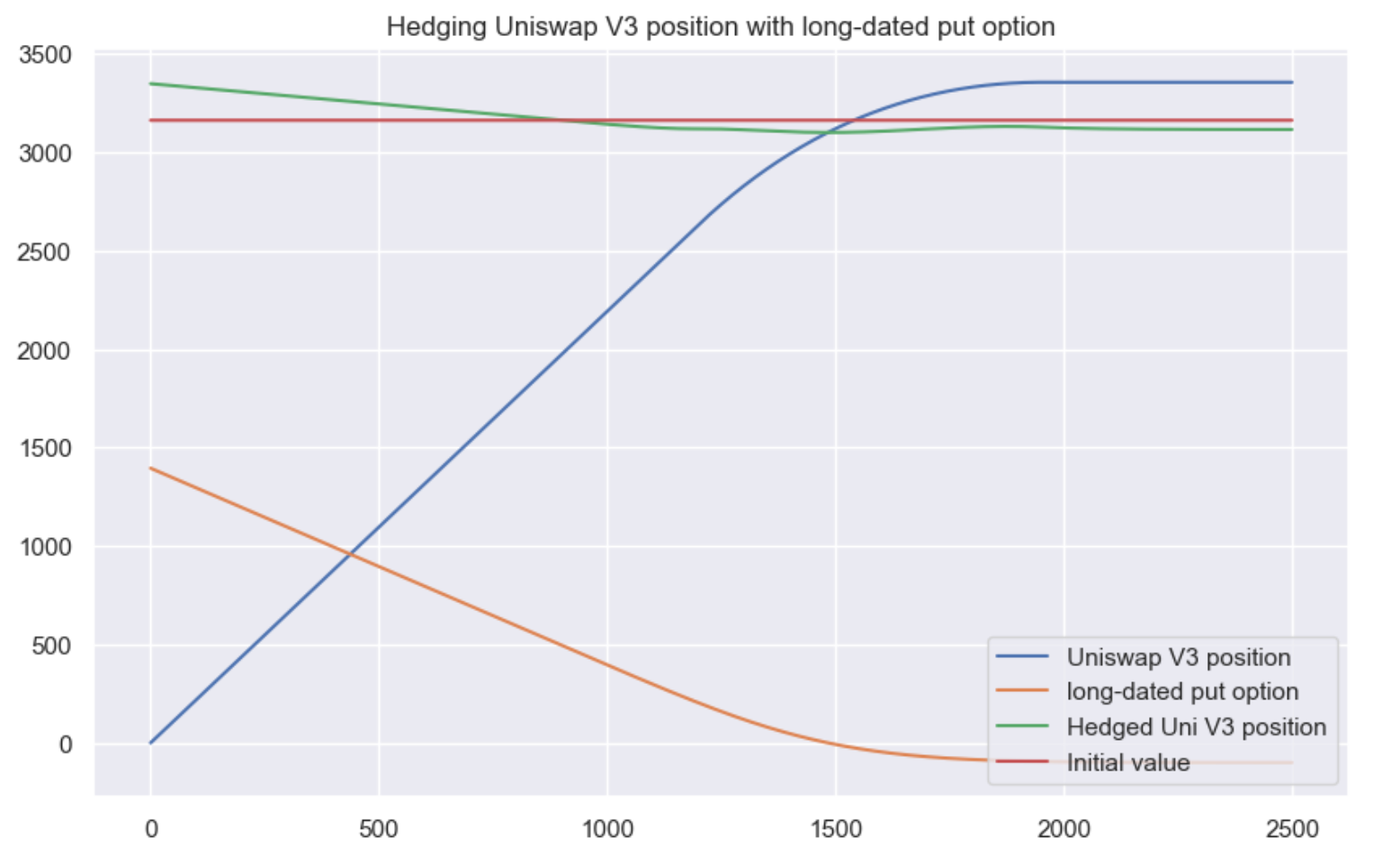
Almost perfect hedging of a Uniswap v3 position with an option
That is, we should buy a put option with a later expiration, hold this option for some time, and then sell it. Then the curvature of the option will be close to the Uniswap V3 position.
Will a fully hedged Uniswap V3 position be profitable?
A detailed analysis shows that in most cases the fees from a Uniswap V3 position cannot compensate for the cost of the option. But not always. Nevertheless, options can be considered a good way to hedge risks (for example, buying a cheap out-of-the-money option for pennies, greatly limiting your losses).
I hope the article was interesting and useful for you. I’ll be glad to read your comments.